About Me

Xufeng Duan (段旭峰)
I am a Research Assistant Professor in the Language Processing Lab at Brain and Mind Institute, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK). I am currently seeking an Assistant Professor position starting in 2026.My research focuses on human language production and large language models (LLMs). I use behavioral, EEG, and fMRI data, along with computational methods, to explore the mechanisms of the human language system. I also work on mechanistic interpretability, which aims to reverse-engineer the internal workings of LLMs to understand how specific computations (e.g., syntax, prediction) are implemented. Additionally, I am trained and licensed in TMS for research purposes in Hong Kong and have completed an internship as a language therapist/researcher specializing in aphasia at the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University.
Email: xufengduan@cuhk.edu.hk
Google Scholar
Curated Research
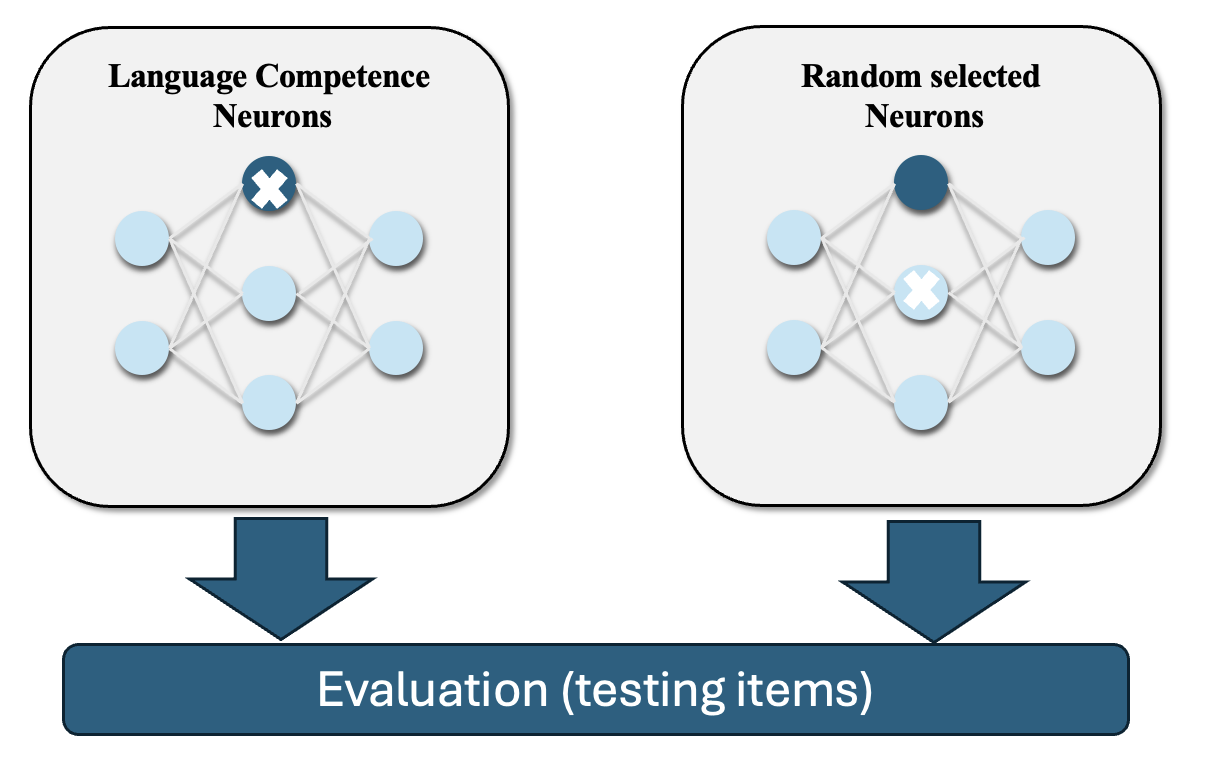
Unveiling Language Competence Neurons: A Psycholinguistic Approach to Model Interpretability
Identifying interpretable units in large language models aligned with psycholinguistic effects, bridging model neurons and human linguistic competence.
Link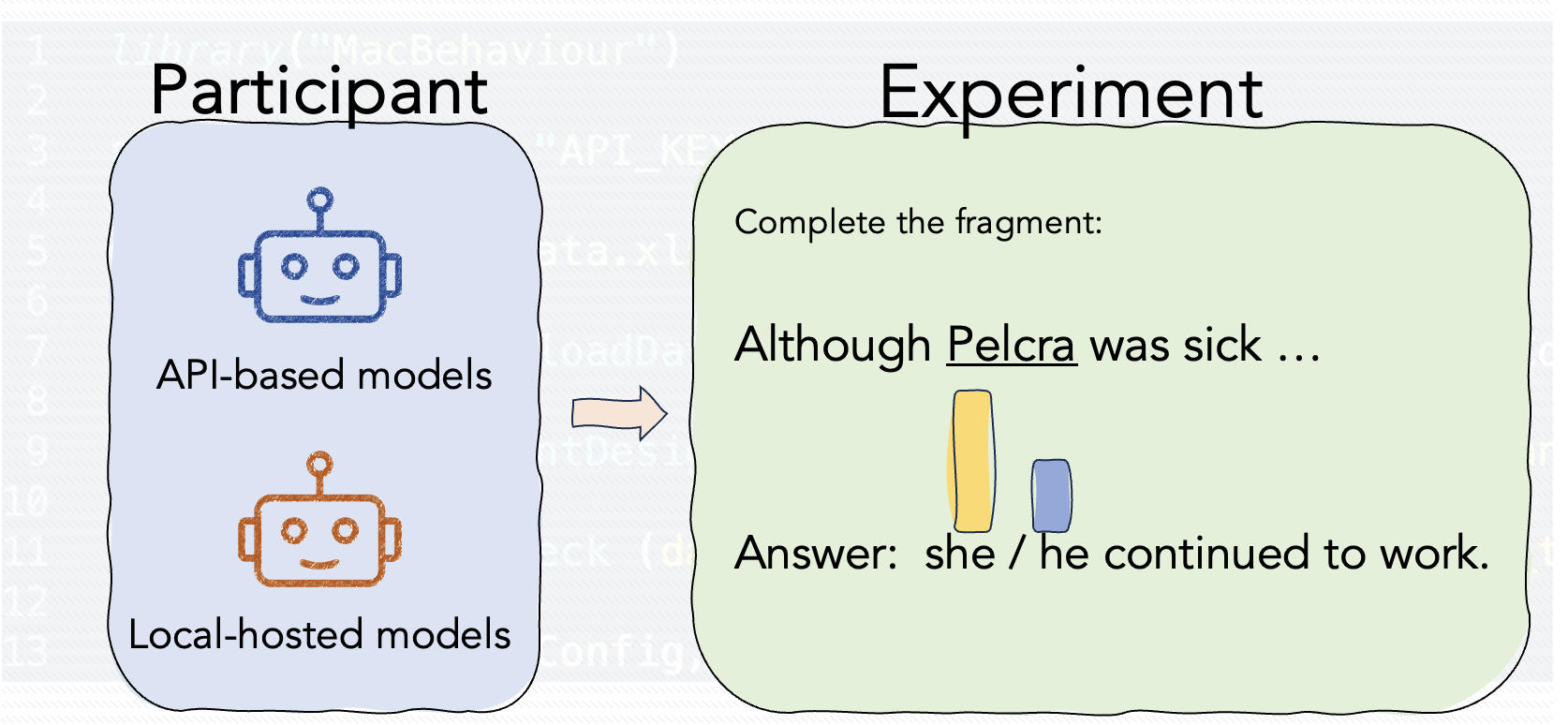
MacBehaviour: An R package for behavioural experimentation on large language models
An open-source R toolkit to help researchers quickly set up behavioral experiments interacting with LLMs, either locally or in the cloud.
LinkPublications
Total: Loading... publications • Auto-generated from bibliography
Loading publications...
Conference Talks
Xufeng Duan MacBehaviour: An R package for behavioural experimentation on large language models. (2024). Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing Asia (AMLaP Asia). Singapore.Xufeng Duan The Neural Basis of Decline in Written Production: Evidence from Chinese Handwriting (2024). The annual meeting of Society for the Neurobiology of Language (SNL) . Brisbane, Australia.
Xufeng Duan Humanlike language use in LLMs (2024). CogSci Hong Kong Meetup Hong Kong, China.
Xufeng Duan Chinese translations of English words: A comparison between human and ChatGPT translations (2023). Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing Asia (AMLaP Asia). Hong Kong, China.
Zhenguang Cai, Xufeng Duan, Lu Sun, and Martin Pickering. Structural priming in ChatGPT (2023). Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing Asia (AMLaP Asia). Hong Kong, China.
Zhenguang Cai, Xufeng Duan, David Haslett, Shuqi Wang & Martin Pickering. Do language models resemble humans in language use (2023)? Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing (AMLaP). Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain.
Zhuang Qiu, Xufeng Duan, and Zhenguang Cai. Does ChatGPT Resemble Humans in Processing Implicatures (2023)? Proceedings of the 4th Natural Logic Meets Machine Learning Workshop, pages 25–34, Nancy, France. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Xufeng Duan(2018). Language rehabilitation training therapies for Chinese aphasia— Using Chinese characters as clues. Beyond A Limited Scope: Chinese for Specific, Academic, & Professional Purposes Hawaii, US.
Xufeng Duan(2018). The Dependence on different symbolic systems during word recognition-pronunciation tests by Chinese native speakers with aphasia——based on eye-movement methodology. Annual Conference of the Chinese Society of Neurological Linguistics. Xuzhou, China.
Xufeng Duan(2018). The Rules of Prominence and Locality Psychological Reality Basis. Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Linguistic Society. Guangzhou, China.
Poster Presentations
Yichi Zhang, Xufeng Duan & Zhenguang Cai. (2024). The causal role of left inferior frontal gyri in Chinese character handwriting: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. The annual meeting of Society for the Neurobiology of Language (SNL) . Brisbane, Australia.Zhuang Qiu, Xufeng Duan & Zhenguang Cai. (2024). Do Large Language Models Resemble Humans in Grammaticality Judgment? Human sentence processing 2024 . University of Michigan, USA.
Xufeng Duan, Zhenguang Cai & Bo Yao. (2023). Electrophysiological responses associated with character amnesia in Chinese handwriting. Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing (AMLaP). Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain.
Hanlin Wu, Xufeng Duan & Zhenguang Cai. (2023). Belief of Speakers' Linguistic Competence Modulates the N400 Effect Elicited by Inconsistent Lexical Use. Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing (AMLaP). Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain.
Zhuang Qiu, Xufeng Duan, Zhenguang Cai & Nan Zhao. (2023). Pragmatic Implicature Processing in ChatGPT. Architectures and Mechanisms for Language Processing (AMLaP). Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain.
Last updated Jan 15, 2026